Improving public transport accessibility is crucial for creating an inclusive and equitable transit system that serves all members of the community. Accessible public transport ensures that everyone, regardless of their physical abilities, age, or socioeconomic status, can navigate the city efficiently and independently. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to enhance public transport accessibility.
1. Invest in Accessible Infrastructure
Upgrade Transit Stations
Modernizing transit stations to accommodate people with disabilities is essential. Ensure that stations are equipped with:
- Elevators and Ramps: Provide elevators and ramps at all entry and exit points to facilitate access for individuals using wheelchairs, scooters, or strollers.
- Accessible Ticketing Systems: Install ticketing machines that are user-friendly for people with visual or physical impairments. Consider adding audio instructions and braille options.
Design Accessible Vehicles
Public transport vehicles should be designed to meet accessibility standards:
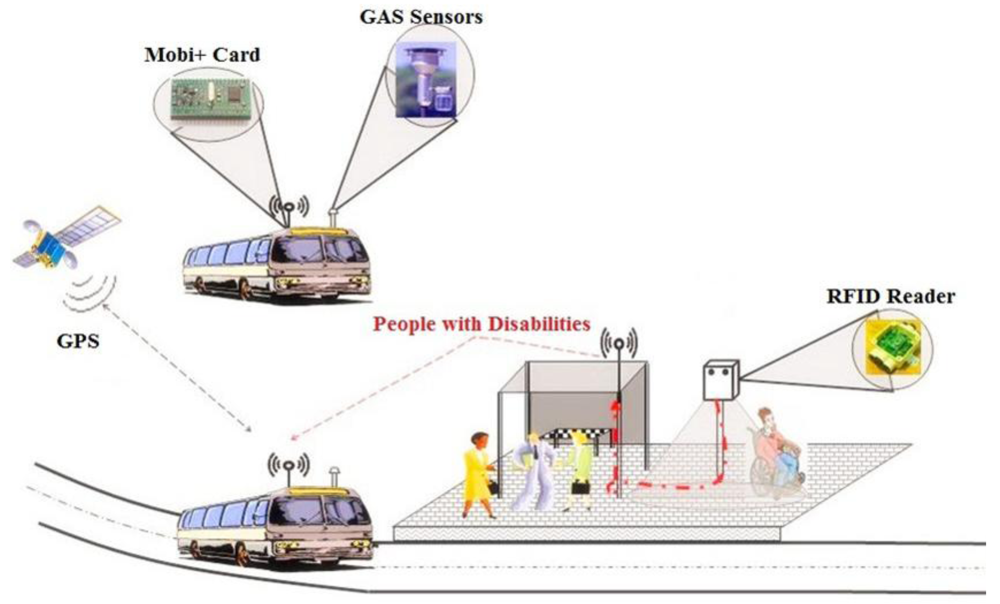
- Low-Floor Buses and Trains: Utilize low-floor designs to make it easier for passengers to board and disembark.
- Dedicated Spaces: Include designated areas for wheelchairs and mobility scooters, with securement features to ensure safety during transit.
- Audio and Visual Announcements: Equip vehicles with systems that provide clear audio and visual information about stops and service changes.
2. Enhance Digital and Technological Solutions
Develop User-Friendly Apps
Create or improve mobile apps to assist passengers with disabilities:
- Real-Time Information: Offer real-time updates on service status, delays, and accessible route options.
- Route Planning: Include features for planning accessible routes, showing details such as elevator locations and step-free access.
Implement Smart Technology
Incorporate smart technology to improve accessibility:
- Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL): Use AVL systems to provide accurate information about the location and arrival times of buses and trains.
- Assistive Technology: Integrate assistive technologies such as voice-activated controls and GPS navigation for visually impaired users.
3. Prioritize Universal Design
Adopt Inclusive Design Principles
Implement universal design principles to ensure that public transport systems are usable by everyone:
- Clear Signage: Use large, high-contrast fonts and clear symbols to make signage easy to read for people with visual impairments.
- Comfortable Seating: Provide seating options that accommodate various needs, including seats with armrests and ample space for people with mobility challenges.
Ensure Consistency Across Services
Maintain consistent accessibility features across different types of transport services:
- Coordination Between Services: Ensure that accessibility features are integrated across buses, trains, trams, and other transit modes for a seamless travel experience.
- Training for Staff: Train transit staff to assist passengers with disabilities and provide information about accessible features and services.
4. Improve Policy and Planning
Develop Inclusive Policies
Formulate policies that prioritize accessibility in public transport planning:
- Accessibility Standards: Enforce compliance with accessibility standards and regulations to ensure that all new and existing transport infrastructure meets required criteria.
- Community Involvement: Involve people with disabilities in the planning and decision-making processes to address their specific needs and preferences.
Monitor and Evaluate
Regularly assess the effectiveness of accessibility improvements:
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback systems to gather input from passengers with disabilities about their experiences and any barriers they encounter.
- Continuous Improvement: Use feedback and data to make ongoing adjustments and improvements to accessibility features and services.
5. Promote Public Awareness and Education
Raise Awareness
Increase awareness about accessibility issues and the importance of inclusive public transport:
- Public Campaigns: Launch campaigns to educate the public and transit operators about accessibility challenges and the benefits of inclusive design.
- Engagement Programs: Partner with advocacy groups and organizations representing people with disabilities to promote understanding and collaboration.
Educate Transit Users
Provide education and resources for transit users to support accessibility:
- Information Materials: Offer informational brochures and online resources about accessible transit options and how to use them.
- Training Workshops: Conduct workshops for community members and transit users on how to navigate the system and assist others with disabilities.
Conclusion
Improving public transport accessibility is essential for creating an inclusive urban environment where all residents can enjoy equal access to transportation services. By investing in accessible infrastructure, leveraging technology, adopting universal design principles, and implementing supportive policies, cities can enhance the quality of life for people with disabilities and ensure that public transport systems are welcoming and functional for everyone. Through continued efforts and community engagement, we can build a more accessible and equitable transit system that meets the needs of all passengers.



